Clinical Evaluations
Cervitec Plus
Ivoclar
www.ivoclar.com
Overview
- 43 Clinical Evaluators
- 656 Total Uses
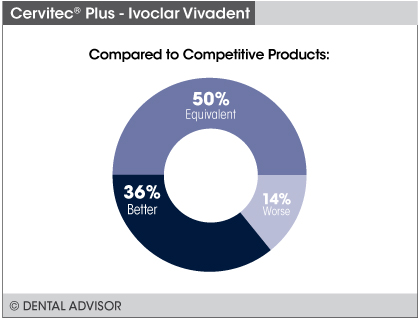
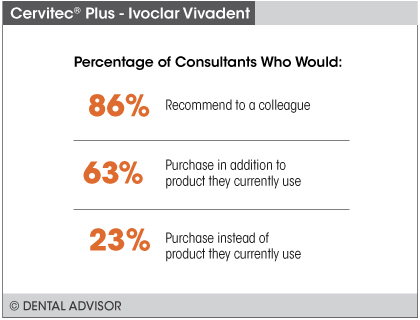
- 91% Clinical Rating
Evaluators’ Comments
- “Super easy and quick application.”
- “Tissue responds very well and quickly.”
- “No taste, so even kids didn’t object.”
- “Patients did not notice the film as much as they do with fluoride varnish.”
- “It was very effective against sensitivity.”
- “Inconvenient that it needs to be refrigerated.”
- “Lower viscosity than fluoride varnish.”
Indications
- Protection of exposed root surfaces
- Treatment of hypersensitive cervical areas
Unique Attributes
- After varnish has been applied and dried, the concentration of chlorhexidine and thymol increases to 10%
- Wide variety of uses because of antimicrobial properties.
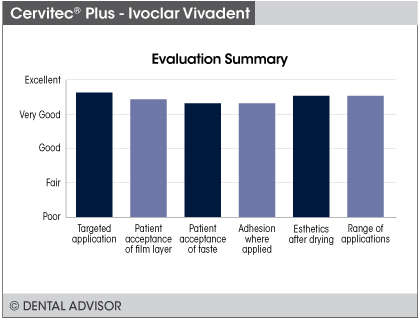
- Low film thickness and clear application ideal for patient acceptance.
- No discoloration of tooth structure after application.
Clinical Tips
- Proper isolation is essential for the best results.
- Use for orthodontic patients with poor oral hygiene that have already started developing decalcifications.
- Have readily available in hygiene appointments for high-risk patients.
- Apply directly onto tooth structure and/or appliances for maximized efficacy.
Description
Cervitec Plus varnish contains a combination of the active ingredients, chlorhexidine and thymol. Chlorhexidine diacetate is an antimicrobial that has long been used in dentistry to reduce bacteria known to cause plaque formation, inflammation, and caries. Thymol, derived from oil of thyme, is a common ingredient found in oral mouth rinses because of its antiseptic characteristics.
- Allows for selective placement to targeted areas for both reduction of bacteria and for desensitization of hypersensitive dentin.
- Available in a 20-count box of 0.25 g single dose packets or in a 7 g tube.
Cervitec Plus is ideal for use:
- After temporary restoration placement
- After root planing and scaling
- In areas susceptible to caries
- Along the margins of implants, crowns and bridges
- Around orthodontic brackets to prevent white spot lesions
- Cervical hypersensitivity